Stainless Steel is the abbreviation of stainless steel and acid resistant steel. The steel that is resistant to weak corrosion media such as air, steam and water or has stainless property is called stainless steel; The steel that is resistant to chemical corrosion medium (acid, alkali, salt and other chemical etching) is called acid resistant steel.
Stainless steel refers to steel that is resistant to weak corrosion media such as air, steam and water and chemical etching media such as acid, alkali and salt, also known as stainless acid resistant steel. In practical applications, steel resistant to weak corrosion medium is often called stainless steel, while steel resistant to chemical medium is called acid resistant steel. Due to the difference in chemical composition between the two, the former is not necessarily resistant to chemical medium corrosion, while the latter is generally stainless. The corrosion resistance of stainless steel depends on the alloy elements contained in the steel.
Generally, according to the metallographic structure, ordinary stainless steels are divided into three types: austenitic stainless steels, ferritic stainless steels and martensitic stainless steels. On the basis of these three basic metallographic structures, dual phase steel, precipitation hardening stainless steel and high alloy steel with iron content less than 50% have been derived for specific needs and purposes.
It is divided into:
Austenitic stainless steel
The matrix is mainly austenitic structure (CY phase) with face centered cubic crystal structure, which is nonmagnetic, and is mainly strengthened (and may lead to certain magnetism) by cold working. The American Iron and Steel Institute is indicated by 200 and 300 series numbers, such as 304.
Ferritic stainless steel
The matrix is mainly ferrite structure (phase a) with body centered cubic crystal structure, which is magnetic, and generally cannot be hardened by heat treatment, but can be slightly strengthened by cold working. The American Iron and Steel Institute is marked 430 and 446.
Martensitic stainless steel
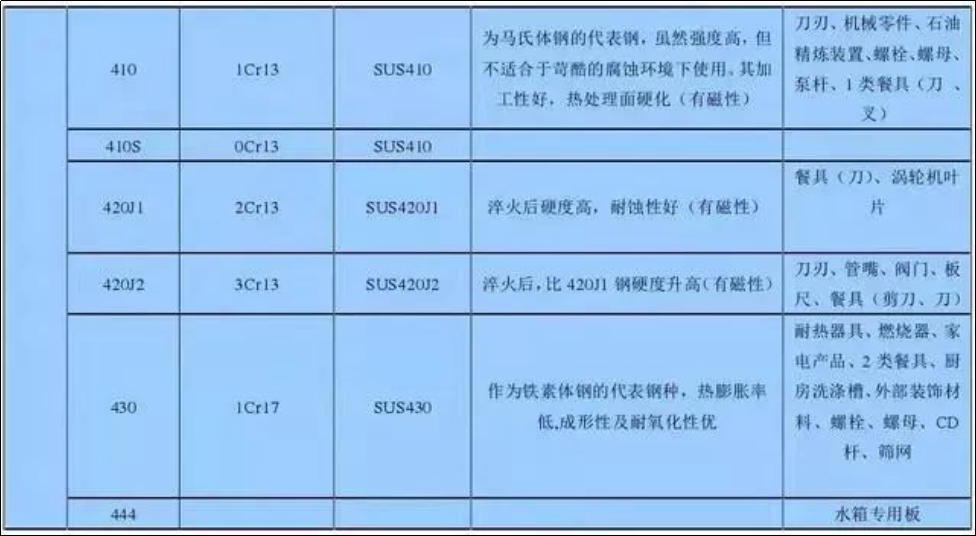
The matrix is martensitic structure (body centered cubic or cubic), magnetic, and its mechanical properties can be adjusted through heat treatment. The American Iron and Steel Institute is indicated by the numbers 410, 420, and 440. Martensite has austenitic structure at high temperature. When it is cooled to room temperature at an appropriate rate, the austenitic structure can be transformed into martensite (i.e., hardened).
Austenitic ferritic (duplex) stainless steel
The matrix has both austenite and ferrite two-phase structures, and the content of less phase matrix is generally more than 15%, which is magnetic and can be strengthened by cold working. 329 is a typical duplex stainless steel. Compared with austenitic stainless steel, dual phase steel has higher strength, and its resistance to intergranular corrosion, chloride stress corrosion and pitting corrosion has been significantly improved.
Precipitation hardening stainless steel
Stainless steel whose matrix is austenitic or martensitic and can be hardened by precipitation hardening treatment. The American Iron and Steel Institute is marked with 600 series numbers, such as 630, i.e. 17-4PH.
Generally speaking, except for alloy, austenitic stainless steel has excellent corrosion resistance. Ferritic stainless steel can be used in the environment with low corrosion. In the environment with mild corrosion, martensitic stainless steel and precipitation hardening stainless steel can be used if the material is required to have high strength or hardness.
Characteristics and purpose
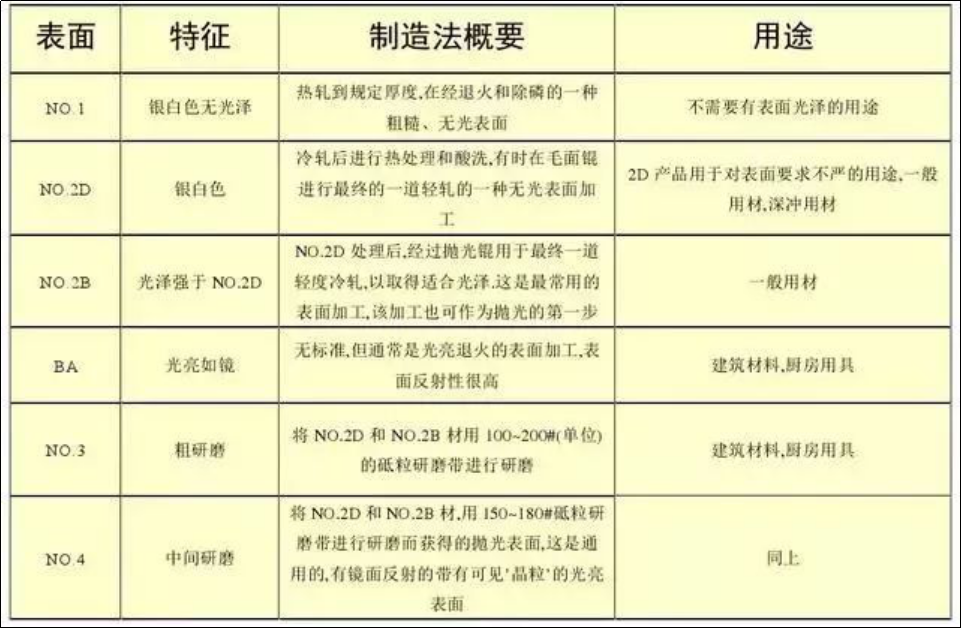
Surface treatment
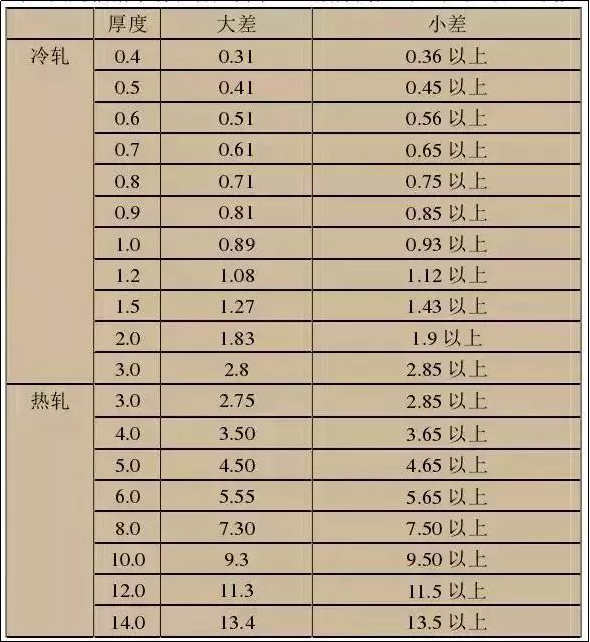
Thickness differentiation
1. Because in the rolling process of the steel plant machinery, the roll is slightly deformed due to heating, resulting in a deviation in the thickness of the rolled plate. Generally, the middle thickness is thin on both sides. When measuring the thickness of the plate, the central part of the plate head shall be measured according to national regulations.
2. Tolerance is generally divided into large tolerance and small tolerance according to market and customer demand: for example
What kind of stainless steel is not easy to rust?
There are three main factors affecting stainless steel corrosion:
1. The content of alloying elements.
Generally speaking, steel with a chromium content of 10.5% is not easy to rust. The higher the content of chromium and nickel, the better the corrosion resistance. For example, the nickel content of 304 material should be 8-10%, and the chromium content should be 18-20%. In general, such stainless steel will not rust.
2. The smelting process of the manufacturer will also affect the corrosion resistance of stainless steel.
Large stainless steel plants with good smelting technology, advanced equipment and advanced process can ensure the control of alloy elements, removal of impurities and control of billet cooling temperature, so the product quality is stable and reliable, the internal quality is good, and it is not easy to rust. On the contrary, some small steel plants are backward in equipment and technology. During smelting, impurities cannot be removed, and the products produced will inevitably rust.
3. External environment, dry and well ventilated environment is not easy to rust.
However, areas with high air humidity, continuous rainy weather, or high pH in the air are prone to rust. 304 stainless steel will rust if the surrounding environment is too poor.
How to deal with rust spots on stainless steel?
1. Chemical methods
Use acid cleaning paste or spray to assist the rusted parts to passivate again to form chromium oxide film to restore their corrosion resistance. After acid cleaning, in order to remove all pollutants and acid residues, it is very important to properly rinse with clean water. After all treatment, re polish with polishing equipment and seal with polishing wax. For those with slight rust spots locally, 1:1 gasoline engine oil mixture can also be used to remove the rust spots with a clean rag.
2. Mechanical method
Blast cleaning, shot blasting with glass or ceramic particles, immersion, brushing and polishing. It is possible to remove the contamination caused by previously removed materials, polishing materials or annihilation materials by mechanical means. All kinds of pollution, especially foreign iron particles, may be the source of corrosion, especially in humid environment. Therefore, the mechanically cleaned surface should preferably be formally cleaned under dry conditions. Mechanical method can only be used to clean the surface, and can not change the corrosion resistance of the material itself. Therefore, it is recommended to re polish with polishing equipment after mechanical cleaning and seal with polishing wax.
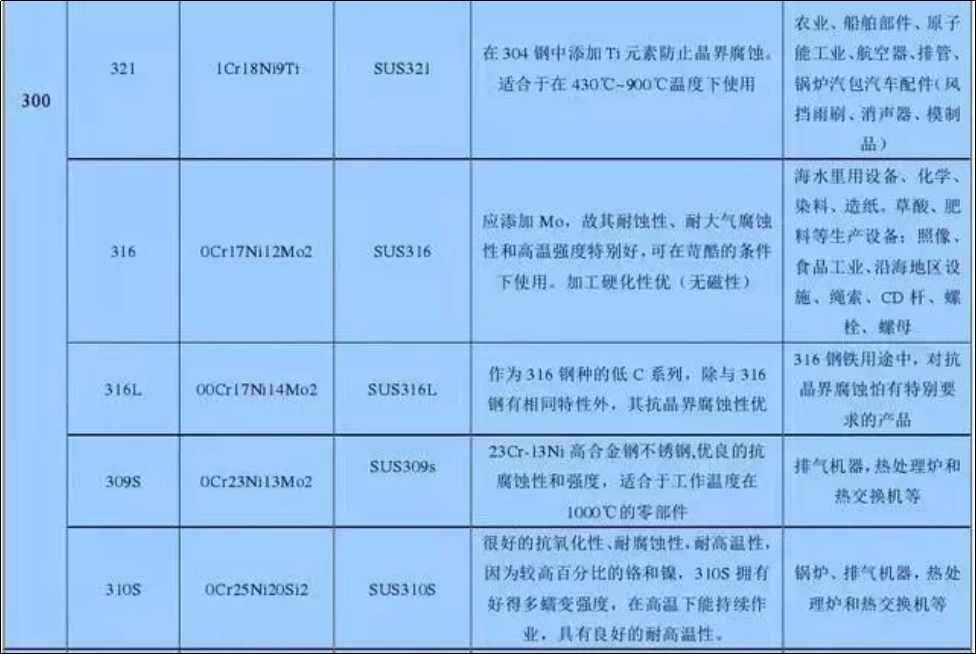
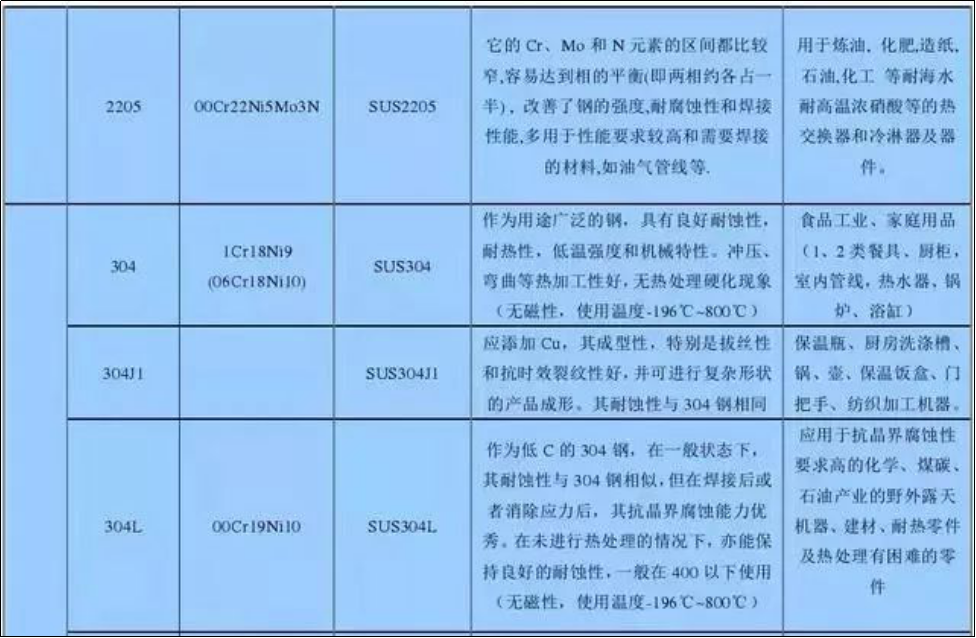
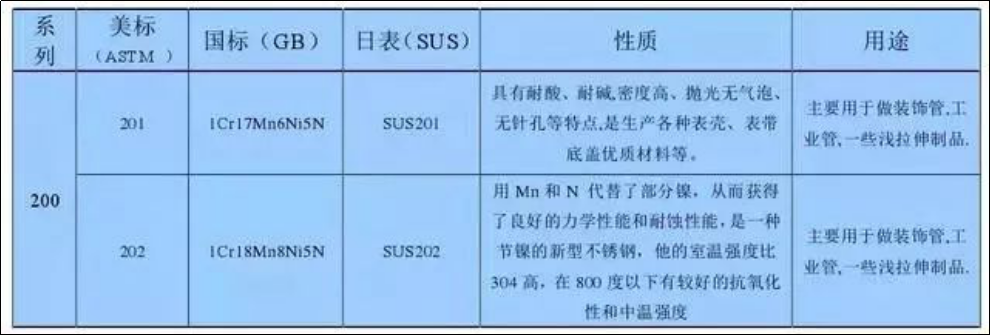
Commonly used stainless steel grades and properties
1. 304 stainless steel. It is one of the most widely used austenitic stainless steels with a large amount of applications. It is suitable for manufacturing deep drawing formed parts, acid transmission pipes, vessels, cnc structural turninig parts, various instrument bodies, etc., as well as non-magnetic and low-temperature equipment and components.
2. 304L stainless steel. The ultra-low carbon austenitic stainless steel developed to solve the serious intergranular corrosion tendency of 304 stainless steel caused by Cr23C6 precipitation under some conditions, its sensitized intergranular corrosion resistance is significantly better than 304 stainless steel. Except for lower strength, other properties are the same as 321 stainless steel. It is mainly used for corrosion resistant equipment and parts that need welding but cannot be solution treated, and can be used to manufacture various instrument bodies.
3. 304H stainless steel. For the internal branch of 304 stainless steel, the carbon mass fraction is 0.04% – 0.10%, and the high temperature performance is superior to 304 stainless steel.
4. 316 stainless steel. The addition of molybdenum on the basis of 10Cr18Ni12 steel makes the steel have good resistance to reducing medium and pitting corrosion. In seawater and other media, the corrosion resistance is superior to 304 stainless steel, mainly used for pitting corrosion resistant materials.
5. 316L stainless steel. Ultra low carbon steel, with good resistance to sensitized intergranular corrosion, is suitable for manufacturing thick section size welding parts and equipment, such as anti-corrosion materials in petrochemical equipment.
6. 316H stainless steel. For the internal branch of 316 stainless steel, the carbon mass fraction is 0.04% – 0.10%, and the high temperature performance is superior to that of 316 stainless steel.
7. 317 stainless steel. The resistance to pitting corrosion and creep is superior to 316L stainless steel. It is used to manufacture petrochemical and organic acid resistant equipment.
8. 321 stainless steel. Titanium stabilized austenitic stainless steel can be replaced by ultra-low carbon austenitic stainless steel because of its improved intergranular corrosion resistance and good high temperature mechanical properties. Except for special occasions such as high temperature or hydrogen corrosion resistance, it is generally not recommended to use.
9. 347 stainless steel. Niobium stabilized austenitic stainless steel. The addition of niobium improves the intergranular corrosion resistance. Its corrosion resistance in acid, alkali, salt and other corrosive media is the same as 321 stainless steel. With good welding performance, it can be used as both corrosion resistant material and heat resistant steel. It is mainly used in thermal power and petrochemical fields, such as making vessels, pipes, heat exchangers, shafts, furnace tubes in industrial furnaces, and furnace tube thermometers.
10. 904L stainless steel. Super complete austenitic stainless steel is a super austenitic stainless steel invented by OUTOKUMPU Company of Finland. Its nickel mass fraction is 24% – 26%, and carbon mass fraction is less than 0.02%. It has excellent corrosion resistance. It has good corrosion resistance in non oxidizing acids such as sulfuric acid, acetic acid, formic acid and phosphoric acid, as well as good resistance to crevice corrosion and stress corrosion. It is applicable to various concentrations of sulfuric acid below 70 ℃, and has good corrosion resistance to acetic acid of any concentration and temperature under normal pressure and to mixed acid of formic acid and acetic acid. The original standard ASMESB-625 classified it as nickel base alloy, and the new standard classified it as stainless steel. In China, there is only a similar brand of 015Cr19Ni26Mo5Cu2 steel. A few European instrument manufacturers use 904L stainless steel as the key material. For example, the measuring tube of E+H mass flowmeter uses 904L stainless steel, and the case of Rolex watches also uses 904L stainless steel.
11. 440C stainless steel. The hardness of martensitic stainless steel, hardenable stainless steel and stainless steel is the highest, and the hardness is HRC57. It is mainly used to make nozzles, bearings, valve cores, valve seats, sleeves, valve stems, cnc machining parts etc.
12. 17-4PH stainless steel. Martensitic precipitation hardening stainless steel, with hardness of HRC44, has high strength, hardness and corrosion resistance, and cannot be used at temperatures higher than 300 ℃. It has good corrosion resistance to atmosphere and diluted acid or salt. Its corrosion resistance is the same as 304 stainless steel and 430 stainless steel. It is used to manufacture offshore platforms, turbine blades, valve cores, valve seats, sleeves, valve stems, etc.
13. 300 Series – Chromium Nickel Austenitic Stainless Steel
301 – Good ductility, used for molding products. It can also be hardened rapidly through mechanical processing, with good weldability. The wear resistance and fatigue strength are superior to 304 stainless steel. 301 stainless steel shows obvious work hardening during deformation, and is used in various occasions requiring high strength
302 – Essentially, it is a variety of 304 stainless steel with higher carbon content, which can obtain higher strength through cold rolling.
302B – is a stainless steel with high silicon content, which has high resistance to high temperature oxidation.
303 and 303Se are free cutting stainless steels containing sulfur and selenium respectively, which are used in occasions where free cutting and high gloss are mainly required. 303Se stainless steel is also used to make machine parts requiring hot upsetting, because under such conditions, this stainless steel has good hot workability.
304N – is a stainless steel containing nitrogen. Nitrogen is added to improve the strength of steel.
305 and 384 – Stainless steel contains high nickel, and its work hardening rate is low, which is suitable for various occasions with high requirements for cold formability.
308 – For making welding rod.
The nickel and chromium contents of 309, 310, 314 and 330 stainless steels are relatively high to improve the oxidation resistance and creep strength of the steels at high temperatures. While 30S5 and 310S are variants of 309 and 310 stainless steels, the difference is that the carbon content is low, so as to minimize the carbide precipitated near the weld. 330 stainless steel has a particularly high carburizing resistance and thermal shock resistance.
Post time: Dec-05-2022